This note is about the problems that I met while using Docker.
What is Docker

Definition[1]
Build, Ship, and Run Any App, Anywhere
Components
- Docker Client
- Docker Daemon
- Docker Image
- Docker Registry
- Docker Container
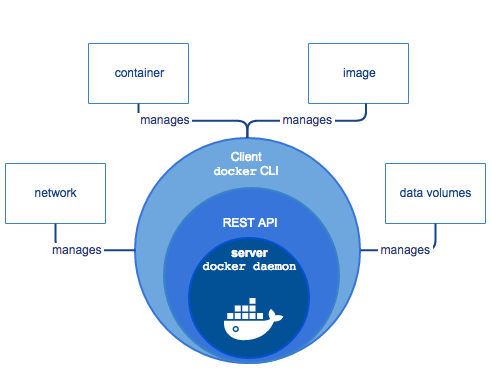
Architecture
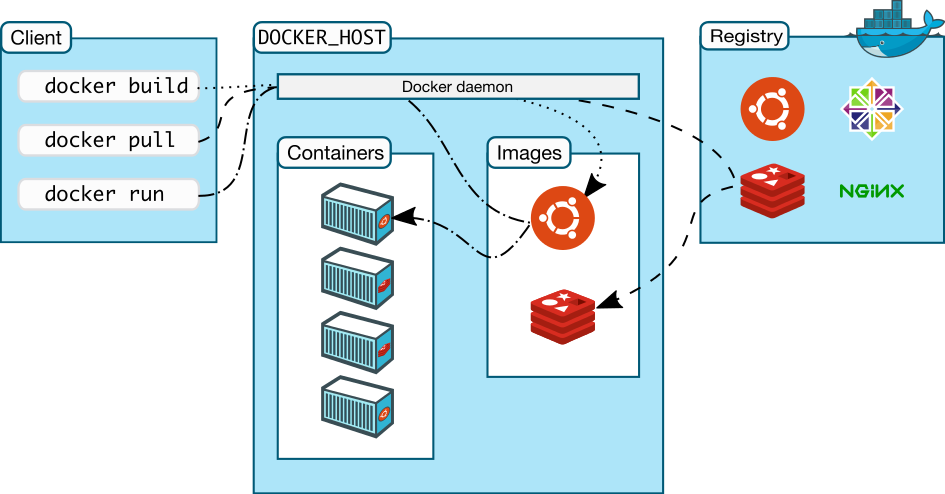
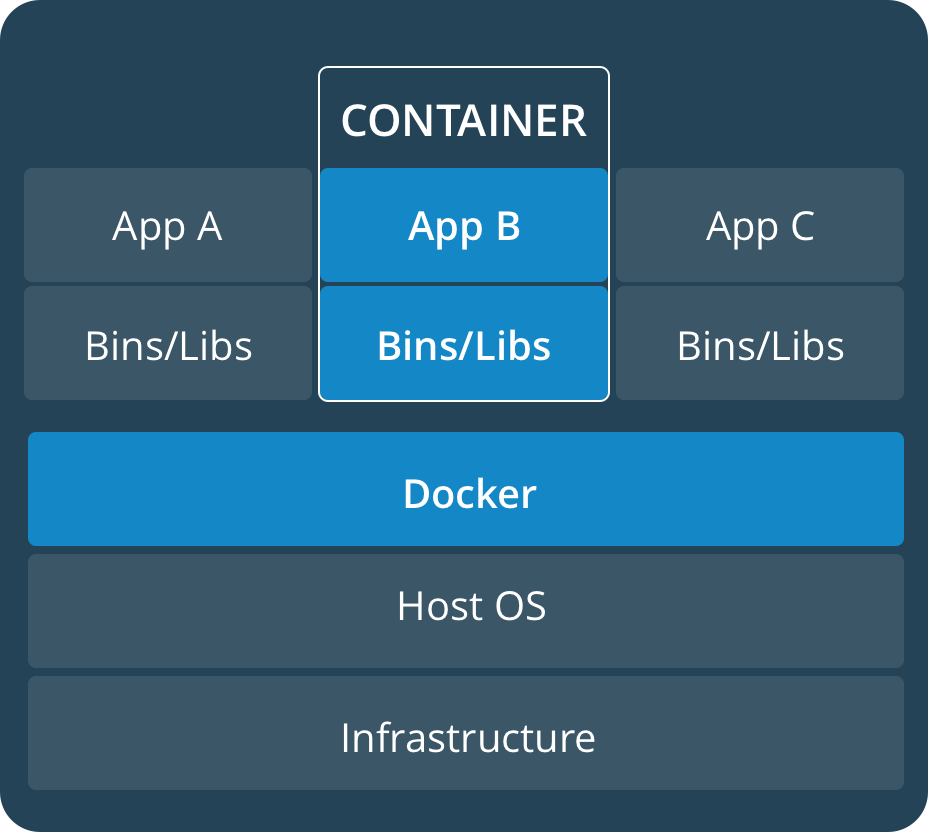
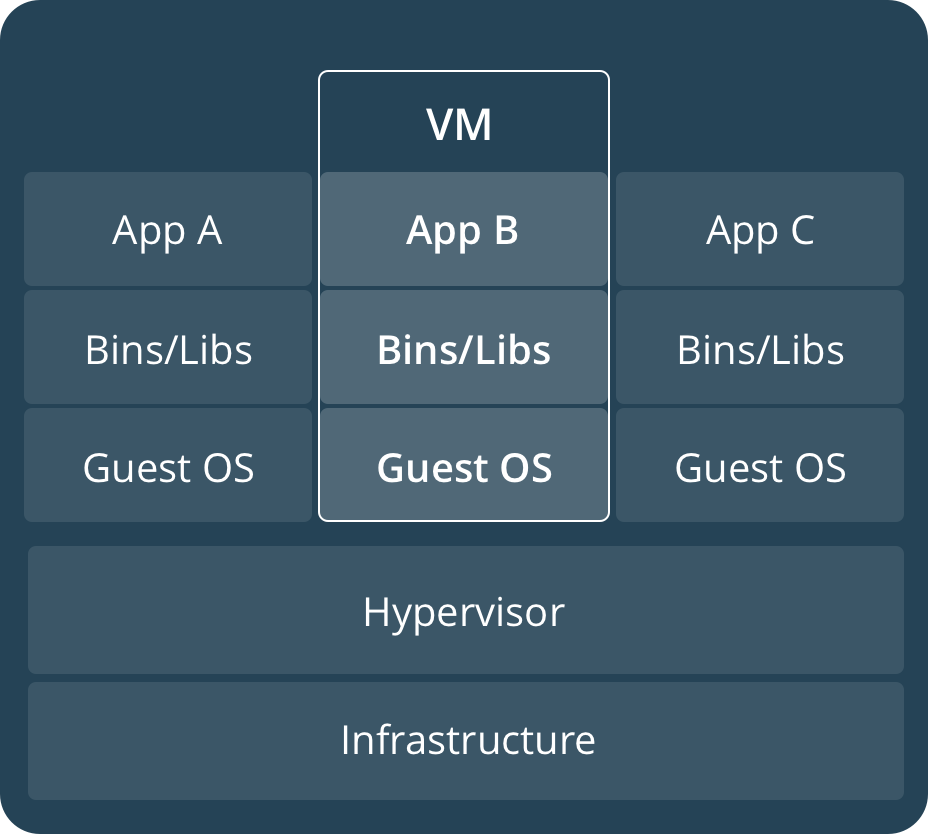
Difference between docker containers and virtual machines
| Docker Containers | Virtual Machines |
|---|---|
 |
 |
Core Tech[2]
-
Linux Namespace(ns)
- pid namespace
- net namespace
- ipc namespace
- mnt namespace
- uts namespace
- user namespace
-
Contral Groups(cgroups)
- blkio
- cpu
- cpuacct
- cpuset
- devices
- freezer
- memory
- net_cls
- ns
-
AUFS(AnotherUnionFS)
-
Security
- Secured by kernel namespaces and cgroups.
- Secured by Docker Deamon APIs.
- Secured by Linux’s solution such as AppArmor, SELinux.
Requirement
See official guide.
Install
See official guide.
Configuration
Use Dockerfile to build the image
# In the host
# Dockerfile is in current folder
$ docker build . -t image_nameOften used commands
- ADD
- ENV
- EXPOSE
- FROM
- RUN
- CMD
Set Java
Use Dockerfile to build the image.
# Set Java environment
ENV JAVA_HOME /home/java/jre/
ENV CLASSPATH .:/home/java/jre/lib
ENV PATH /home/java/jre/bin:/usr/local/sbin:/usr/local/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin:/sbin:/binSet Locale
Configure the locales in the host.
Use Dockerfile to build the image.
# Set locales
RUN locale-gen en_US en_US.UTF-8
RUN locale-gen zh_CN zh_CN.UTF-8
RUN locale-gen nb_NO nb_NO.UTF-8
ENV LANG en_US.utf8Set Port
Use Dockerfile to build the image.
# Expose the port to the public
EXPOSE 80MySQL
Install in the host.
Vsftpd
Install in the host.
Often used commands
RUN
This command creates a container from a docker image.
$ docker run -t -i -p 80:80 -p 443:443 -p 8092:8092 -v /home:/home --name container_name --hostname web username/image-v Better use absolute path.
START
This command starts a container which is stopped.
$ docker start container_id/container_nameSTOP
This command stops a container which is running.
$ docker stop container_id/container_nameATTACH
This command enters into a started container.
$ docker attach container_id/container_nameWhile you are in a container, you cannot leave it with
ctrl+c. This will stop the container. Usectrl+p+qinstead.Use
attachto enter it again.
PS
This command displays containers.
# Display running containers
$ docker ps
# Display all containers
$ docker ps -aIMAGES
This command displays images.
$ docker imagesRM
This command removes a container.
$ docker rm container_id/container_nameThe container has to be stopped.
RMI
This command removes an image
$ docker rmi image_nameCOMMIT
This command commits changes in a container to a image.
$ docker commit container_name image_namePUSH
This command pushes local image to a repository.
$ docker push username/repo_name:tagPULL
This command pulls image from a repository.
$ docker pull username/repo_nameSAVE
This command saves image to a local file.
$ docker save -o file_name.tar image_name:tag_name1 image_name:tag_name2LOAD
This command loads image from a local file.
$ docker load --input file_name.tarREMOVE UNUSED IMAGES
This command removes all unused images.
$ docker image prune -aDockerHub
Using different tags to store different versions.
Reference
-
https://www.docker.com/
-
http://www.infoq.com/cn/articles/docker-core-technology-preview
竟然无法拒绝你的打赏


